Disk Utility User Guide
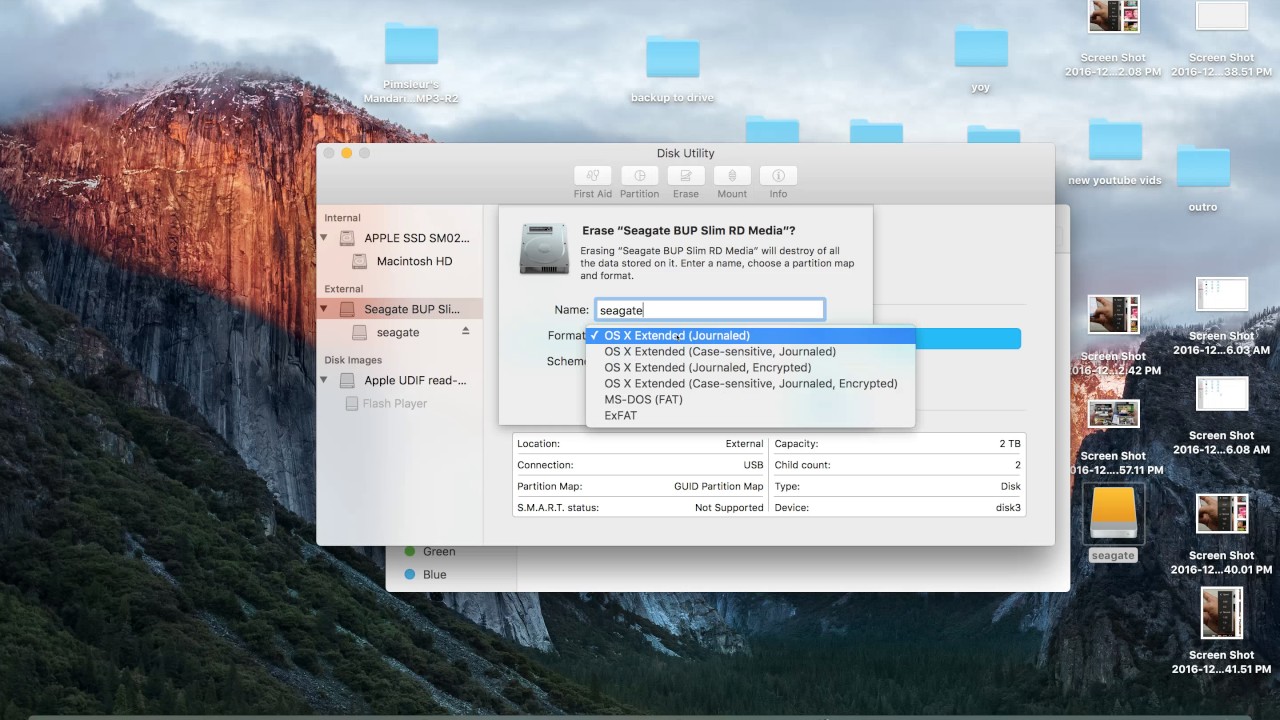
Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats:
Sep 19, 2011 If the drive's format comes up as MS-DOS (FAT) or, less likely, ExFAT, you may be able to simply leave the drive as-is and not bother reformatting it. If the drive is listed as NTFS-formatted. Oct 23, 2017 exFAT is the modernized version of FAT32 and is used the most out of all three, though it is not as well-known as its predecessor. NTFS is the default system on many storage systems, and it is used by Windows, due to the fact that it is the most modern of the three. File Allocation Table 32 (FAT32).
Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later.
Mac OS Extended: The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier.
MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows.

Apple File System (APFS)
Apple File System (APFS), the default file system for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing and improved file system fundamentals. While APFS is optimised for the Flash/SSD storage used in recent Mac computers, it can also be used with older systems with traditional hard disk drives (HDD) and external, direct-attached storage. macOS 10.13 or later supports APFS for both bootable and data volumes.
Exfat Or Ms Dos Fat For Mac And Windows 10
APFS allocates disk space within a container (partition) on demand. When a single APFS container has multiple volumes, the container’s free space is shared and automatically allocated to any of the individual volumes as needed. If desired, you can specify reserve and quota sizes for each volume. Each volume uses only part of the overall container, so the available space is the total size of the container, minus the size of all the volumes in the container.
Choose one of the following APFS formats for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later.
APFS: Uses the APFS format. Choose this option if you don’t need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
APFS (Encrypted): Uses the APFS format and encrypts the volume.
APFS (Case-sensitive): Uses the APFS format and is case-sensitive to file and folder names. For example, folders named “Homework” and “HOMEWORK” are two different folders.
APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted): Uses the APFS format, is case-sensitive to file and folder names and encrypts the volume. For example, folders named “Homework” and “HOMEWORK” are two different folders.
You can easily add or delete volumes in APFS containers. Each volume within an APFS container can have its own APFS format — APFS, APFS (Encrypted), APFS (Case-sensitive) or APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
Mac OS Extended
Exfat
Choose one of the following Mac OS Extended file system formats for compatibility with Mac computers using macOS 10.12 or earlier.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled): Uses the Mac format (Journaled HFS Plus) to protect the integrity of the hierarchical file system. Choose this option if you don’t need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled): Uses the Mac format and is case-sensitive to folder names. For example, folders named “Homework” and “HOMEWORK” are two different folders.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, is case-sensitive to folder names, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Exfat Or Ms Dos Fat For Mac And Windows 8
Windows-compatible formats
Choose one of the following Windows-compatible file system formats if you are formatting a disk to use with Windows.
MS-DOS (FAT): Use for Windows volumes that are 32GB or less.
ExFAT: Use for Windows volumes that are over 32GB.